Persistent abdominal pain, bloating, or unexplained discomfort can be concerning. If you’ve been experiencing these symptoms, your doctor may recommend an abdominal ultrasound—a safe, non-invasive imaging test that helps your provider diagnose and monitor various conditions affecting your abdominal organs. In this article, we will go over:
- What is an ultrasound?
- What can an abdominal ultrasound detect?
- How does it help guide treatment?
- What can you expect during an ultrasound appointment at Touchstone Medical Imaging?
What Is an Ultrasound?
An ultrasound is a medical imaging test that uses sound waves to create real-time images of internal organs and tissues. It is commonly used to evaluate different parts of the body, including the abdomen, and does not involve radiation.
What Is an Abdominal Ultrasound?
An abdominal ultrasound focuses specifically on imaging organs like the liver, gallbladder, pancreas, kidneys, spleen, and abdominal blood vessels. Unlike X-rays or CT scans, ultrasounds do not use radiation, making them a safe option for all patients, including pregnant women.
When Should You Get an Abdominal Ultrasound?
An abdominal ultrasound can be an important diagnostic tool for identifying issues in the abdominal organs. If you experience any of the following symptoms, your doctor may recommend an abdominal ultrasound to better understand the cause of your symptoms.
- Persistent or Severe Abdominal Pain: Abdominal pain that doesn’t improve or worsens over time may be a sign of a more serious underlying condition, such as gallstones, kidney issues, or appendicitis.
- Unexplained Weight Loss: Losing weight without changing your diet or exercise routine could indicate issues with your digestive organs or metabolism, including liver or pancreatic problems. It may also be a sign of cancer or infection.
- Jaundice (Yellowing of the Skin and Eyes): Jaundice is a symptom that occurs when there is a build-up of bilirubin in the bloodstream, usually due to liver or gallbladder conditions. It can be a sign of hepatitis, cirrhosis, or bile duct obstruction.
- Blood in Your Urine: Hematuria, or the presence of blood in the urine, can be a sign of several conditions, including kidney stones, urinary tract infections, or even more serious issues like bladder cancer. An ultrasound can help detect kidney or urinary tract abnormalities.
- Suspected Gallbladder, Kidney, or Liver Issues: If you have a history of gallstones, kidney stones, liver disease, or have been diagnosed with any abdominal organ issues, your doctor may recommend an ultrasound to monitor the condition. This test can help identify changes in the organs, such as cysts, tumors, or blockages, which may require medical intervention.
Common Conditions Diagnosed with Abdominal Ultrasound
Doctors use abdominal ultrasounds to detect a variety of conditions, including:
1. Gallbladder and Biliary Conditions
- Gallstones: Hardened deposits in the gallbladder that can cause pain and digestive issues.
- Cholecystitis: Inflammation of the gallbladder, often due to gallstones blocking bile flow.
- Biliary Obstruction: Blockages in the bile ducts that can lead to jaundice.
2. Liver Conditions
- Fatty Liver Disease: Excess fat accumulation in the liver, linked to obesity and diabetes.
- Cirrhosis: Scarring of the liver due to chronic liver disease.
- Hepatitis C: A viral infection that causes liver inflammation and potential long-term damage.
- Hepatomegaly: Enlargement of the liver, which can indicate infection, fatty liver disease, or other liver disorders.
- Abnormal LFTs: Abnormal liver function tests can indicate various liver conditions, including fatty liver, hepatitis, or cirrhosis.
3. Pancreatic Disorders
- Pancreatitis: Inflammation of the pancreas, often caused by gallstones or alcohol use.
- Pancreatic Tumors: Ultrasound can detect abnormal growths requiring further imaging.
4. Kidney and Urinary Conditions
- Kidney Stones: Solid mineral deposits that can cause severe pain and urinary problems.
- Kidney Cysts or Tumors: Fluid-filled sacs or abnormal growths in the kidneys.
- Hydronephrosis: Swelling of the kidney due to urine buildup.
- Polycystic Disease: A genetic condition where multiple cysts form in the kidneys, potentially leading to kidney failure.
5. Spleen Conditions
- Splenomegaly: Enlargement of the spleen, which may be caused by infections, blood disorders, or liver disease.
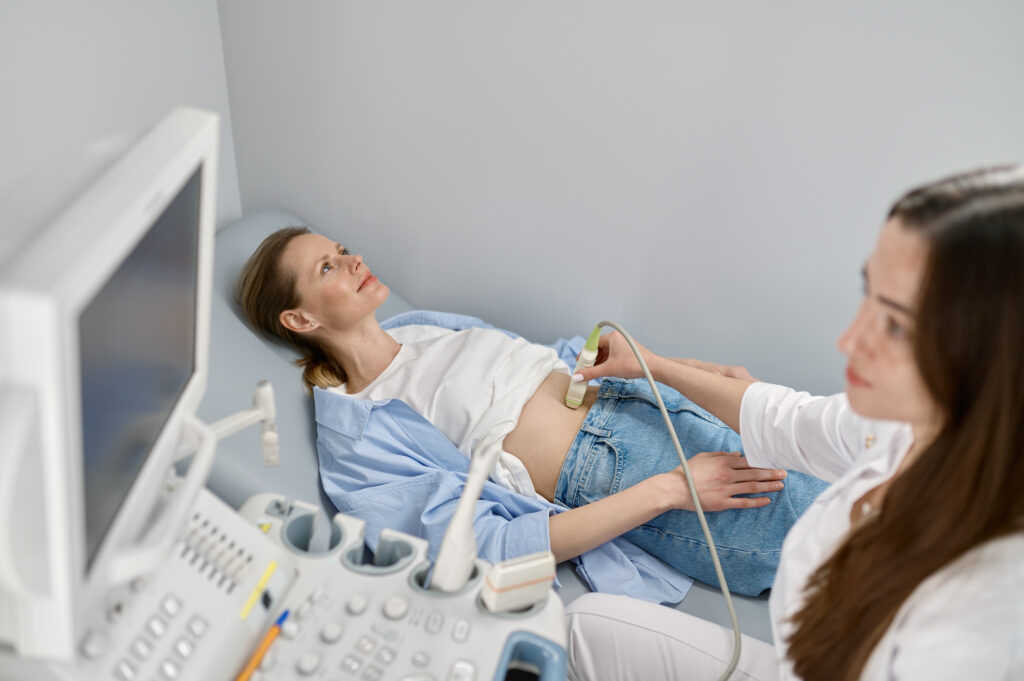
How does ultrasound guide and monitor treatment?
While ultrasounds primarily serve as a diagnostic tool, they also assist with treatment and management of various abdominal conditions.
Monitoring Disease Progression
Once a condition has been diagnosed, ultrasound imaging is often used to monitor its progression over time. For example, fatty liver disease or kidney cysts can be regularly evaluated using ultrasound to track changes in size, structure, or the development of new abnormalities. This ongoing monitoring helps doctors determine whether a treatment plan is working or if adjustments are needed. In cases like chronic liver disease or kidney conditions, ultrasound can provide valuable insights into whether a condition is worsening or stabilizing, allowing for timely interventions.
Post-Surgical Evaluation
After surgeries like gallbladder removal or the repair of a hernia, an abdominal ultrasound can be used to assess complications such as fluid collection, infection, or organ damage. Ultrasound provides a non-invasive option to quickly check for any post-surgical issues, such as bile leaks or internal bleeding, ensuring that your recovery moves along. Ultrasound imaging also helps doctors evaluate the healing process of abdominal tissues, helping them determine if additional treatments or interventions are necessary.
Assessing Tumor or Cyst Response to Treatment
For patients with liver tumors, kidney tumors, or pancreatic cysts, ultrasound is used to monitor how these masses respond to treatment. Whether you are undergoing chemotherapy, radiation, or medication, ultrasound allows your doctor to assess whether a tumor is shrinking, growing, or remaining stable. This is essential for deciding the next steps in a treatment plan, ensuring that therapies are working as intended.
What to Expect During an Abdominal Ultrasound Appointment at Touchstone Medical Imaging
Before the appointment
You may be asked to fast before the exam. Fasting means avoiding eating or drinking for several hours. Ask your healthcare provider if this is necessary. You will also be informed of any specific instructions for fasting in preparation for your abdominal ultrasound when you schedule your appointment. Avoiding food or drink before your abdominal ultrasound helps prevent gas buildup in the belly area. Gas can obscure the images captured by ultrasound.
The day of your abdominal ultrasound
Bring your imaging order (if you have a paper version), insurance card, and any other relevant documents. Touchstone medical imaging offers affordable self-pay options to ensure you get the care you need. If you don’t have insurance, ask about our self-pay options when you check in for your ultrasound exam.
During your abdominal ultrasound
A trained ultrasound technician will apply a gel to your abdomen. This gel helps the transducer to glide over your skin and improves the quality of the ultrasound images captured. The ultrasound exam typically lasts 20-30 minutes and you can return to normal activities immediately after.
After your abdominal ultrasound
Once your results are complete, your doctor may request additional tests or scans to determine the severity of the condition causing symptoms. Any follow up imaging or tests help your healthcare provider gather information to create the most accurate treatment plan for you.
Schedule Your Abdominal Ultrasound Today at Touchstone Imaging
Touchstone Medical Imaging provides comprehensive ultrasounds in Arkansas, Colorado, Florida, Montana, Oklahoma, and Texas.
Reach out to us at Touchstone, and we’ll help you schedule an appointment at an imaging center near you, today.
We’re here to help you get the answers you need.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
A: No, the results will be reviewed by a radiologist and sent to your doctor first. Once your doctor receives the images, they can discuss the results with you.
A: Depending on the type of ultrasound, you may need to fast for 6-8 hours, so it’s important to follow your healthcare provider’s instructions.
A: Yes, you can typically drive yourself home after an abdominal ultrasound, as no sedation or recovery is involved.
A: Abdominal ultrasounds are highly accurate for detecting many conditions. Additional tests may sometimes be needed for further insights.

